Asian Fairy Bluebird

by Flees Photos
Title
Asian Fairy Bluebird
Artist
Flees Photos
Medium
Photograph - Home Decor And Giclee Wall Art By Chris Flees
Description
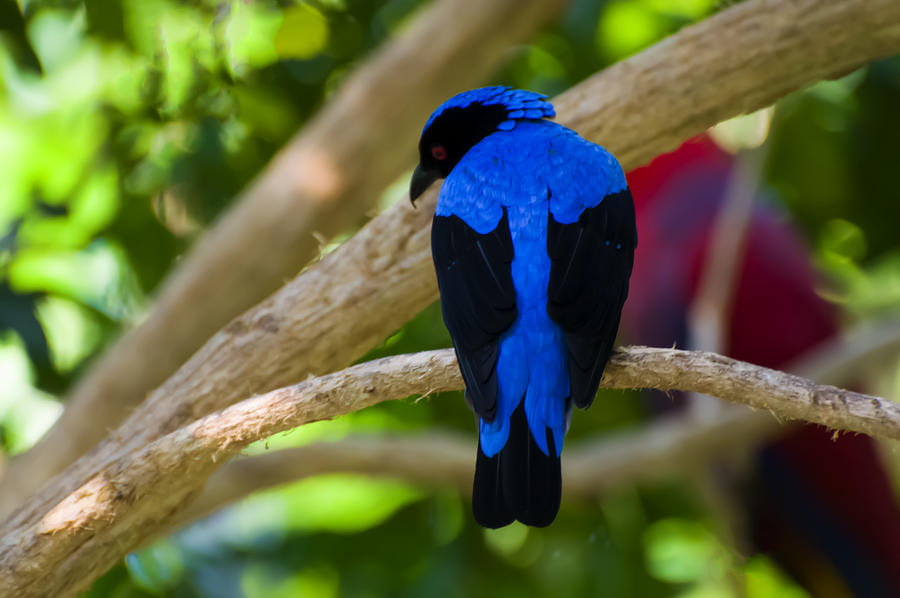
This is an image of an Asian Fairy Bluebird (Irena puella). This is the male. The Asian Fairy bluebird is somewhat like a cardinal in that the male is the very colorful bird and the females colors are very muted. They are extremely beautiful birds. Their diet consists mainly of fruit and they can be found in the upper portion of trees within their natural range.
The Asian Fairy Bluebird (Irena puella) is a species of passerine bird found in various parts of Southeast Asia. Here are some facts about the Asian Fairy Bluebird:
Appearance: The Asian Fairy Bluebird is known for its vibrant and iridescent plumage. The males have deep blue feathers on their head, neck, and upperparts, while the females have a more subdued blue or greenish-blue color. Both genders have a black mask around their eyes.
Size: The Asian Fairy Bluebird is relatively large for a songbird, measuring about 28-32 centimeters (11-12.5 inches) in length.
Diet: These birds primarily feed on fruits and berries. They play an important ecological role in seed dispersal, helping to spread the seeds of various plants throughout their habitat.
Habitat: Asian Fairy Bluebirds inhabit various types of forested habitats, including rainforests, mangroves, and wooded areas. They can be found in countries such as India, Thailand, Malaysia, Indonesia, and the Philippines.
Behavior: Asian Fairy Bluebirds are known for their graceful flight and agile movements in the forest canopy. They often travel in pairs or small groups, and their melodious calls can be heard echoing through the trees.
Breeding: These birds build cup-shaped nests using leaves, twigs, and other plant materials. The female usually lays 2-3 eggs, which are incubated by both parents. Both parents also participate in caring for the young after they hatch.
Conservation status: The Asian Fairy Bluebird is generally considered to be a species of least concern in terms of conservation status. However, deforestation and habitat loss pose threats to their populations, particularly in areas where their forest habitats are being degraded or destroyed.
Uploaded
December 18th, 2014
Embed
Share